Notes
A legal definition of the term "social benefits" is found in Article 11 of Book 1 of the Social Code (SGB I). According to this definition, social benefits are services, benefits in kind and cash benefits provided on the basis of the provisions of the Social Code and the laws referenced in Article 68 SGB I. Article 11 SGB I also includes personal assistance and support with upbringing as relevant services.
Articles 18–29 SGB I list the different types of social benefits and the institutions responsible for their provision:
- Article 18 Training grants
- Article 19 Promotion of employment
- Article 19a Basic security for job-seekers
- Article 19b Services for employees transitioning to retirement
- Article 21 Statutory health insurance
- Article 21a Social care insurance
- Article 21b Termination of pregnancy
- Article 22 Statutory accident insurance
- Article 23 Statutory pension insurance including old-age insurance for farmers
- Article 24 Provision in case of loss of health
- Article 25 Child benefit, child benefit supplement, education and participation grants, parental benefit and child care subsidy
- Article 26 Housing benefit
- Article 27 Child and youth services
- Article 28 Social welfare
- Article 28a Integration support
- Article 29 Rehabilitation and participation for persons with disability
The Asylum Seeker Benefits Act (Asylbewerberleistungsgesetz/AsylbLG) is not included in the SGB I catalogue and thus does not constitute a formal element of social law. However, the scope of services it covers means it forms part of substantive social law. AsylbLG is an independent law regulating the substantive services for service beneficiaries. Government spending on AsylbLG services was just under €4.9bn (gross) in 2018.
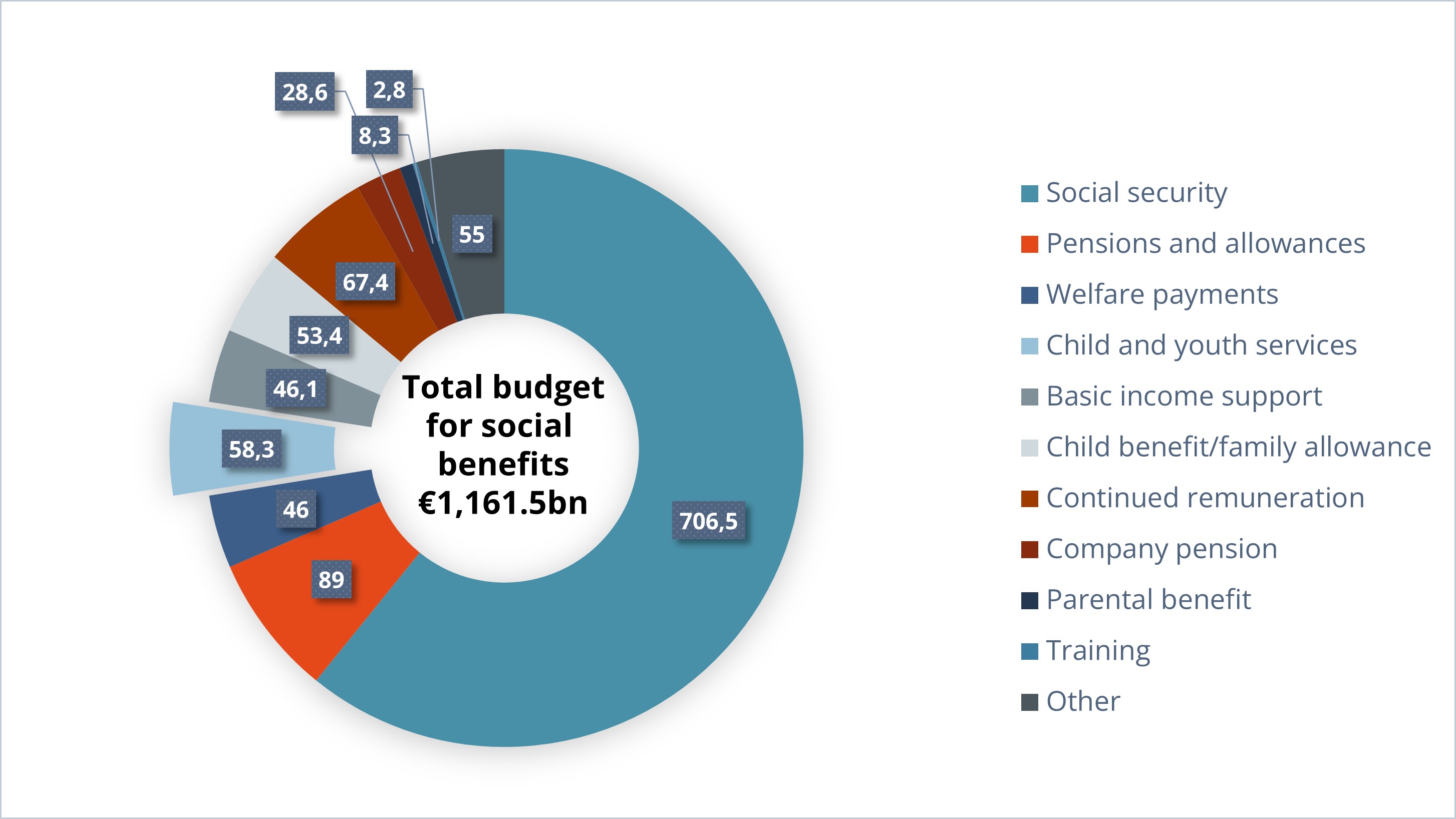
In 2021 social benefits accounted for 32.5% of GDP. Total social benefits in 2021 amounted to €1,161.5bn.
Example shares (€bn):
Social security systems: | total 706.5 |
Assistance and welfare benefits: | total 214.9 |
| 46.1 |
| 46.0 |
| 58.3 |
| 8.3 |
| 53.4 |
| 2.8 |
Further reading
- Bundesministerium für Arbeit und Soziales (BMAS) (2022). Sozialbudget 2021 (last accessed: 31 May 2023).
![[Translate to Englisch:] [Translate to Englisch:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/e/b/csm_2021_09_28_Myles-Tan-WNAO036c6FM-unsplash_kleinIII_0ed92e37b3.jpg)